This time I will explain a bit about CBM in Indonesia. Some of you might have a better knowledge and I hope to get a comment on this blog. However, some of you might also think that Indonesia is not a country with a bountiful CBM resources. I will let you justify this by letting you read my writing here.
Do we (Indonesia) really have CBM ?
Why am I doing this research if we don’t have significant amount of potential resources for CBM? Unfortunately, we are the second largest country in Asia and 7th largest in the world for its CBM resources (Wood Mackenzie, 2015; CBM Asia, 2016; Stevens et al., 2001; Stevens and Hadiyanto, 2004). You may see the countries’ rank below:

(Mastalerz, 2014)
Where are they located?
Indonesia is a beautiful countries with ±17,000 islands :D, that is why we are the archipelago country! – one of the reason that I am so thankful of being born in Indonesia ! Many beautiful beaches, mountains, lakes, rivers, waterfalls, hills, ethnics, languages, animals, etc! – Back to the original topic, haha sorry, I was almost lost in my imagination being back in Indonesia!
Yes, Indonesia is an archipelago country, and this 453tcf is located in four different islands (the four main land). They are located in Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, and Sulawesi (which are dense populated -__- )
Let me show off of my country :p – such a beautiful shape of a country. See Kalimantan? I see Kalimantan like a hen 😀 running 😀
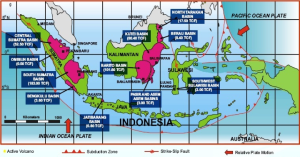
(www.wkmigas.com, 2016)
The pink colour is where the CBM resources are located. And the most CBM resources are located in Sumatra and Kalimantan.
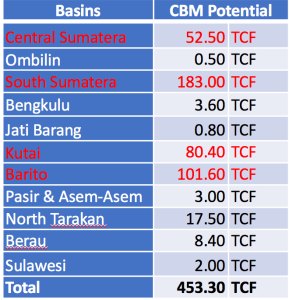
(Wood Mackenzie, 2015; www.wkmigas.com, 2016)
The red text is just to show the CBM basins with the four largest CBM resources in Indonesia.
What type of coal ?
First, Indonesia has thick, abundant and laterally continuous coal beds. Second, CBM in Indonesia is relatively shallow with an optimal depth 1000ft to 5000ft (CBM Asia Development Corp, 2013). The CBM reservoir depth in South Sumatra CBM Basin and East Kalimantan, Kutai Basin are 2000ft and 1000-2500ft respectively (CBM Asia Development Corp, 2013). Third, the coal rank in Indonesia mostly has a low rank. (I will write a bit about low rank in a coal rank. Will put this on my to do list for this weekend). Forth, Indonesia’s basins have a favourable reservoir for accumulation and preservation of CBM. Fifth, Indonesia’s basins have fracturing and faulting evidences in coal. Sixth, Indonesia has a coal bearing gas producing field. Lastly, Indonesia has a good gas content in its main CBM Basin.
To see as a whole geology of Indonesian CBM can be seen below:

As I have written before, I will write separately about the coal rank to help you understanding better. I was a bit struggle to learn the technical part of my research as I have never taken a geology degree. Slowly, but sure, I will have a better understanding by the time I finish my PhD.
The characteristic of the coal in Indonesia has similarities with the Powder River Basin, in the US, and yes, Harrington (2016) noted that Powder River Basin has proven that low rank of coal can be succeeded. If the US can, why can’t we? 😉
Why develops CBM?
The Government of Indonesia (GoI) has a plan to use the CBM to fulfil domestic needs, and in this case is for electricity supply. The GoI has forecasted the need for electricity in Indonesia is to increase 4.67 times in 2019 from 2015 (Tharakan, 2015).
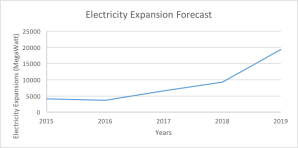
(Tharakan, 2015)
Following if you want to see, the electricity generated in Indonesia:
(International Energy Agency, 2014)
We can see, in Sumatra and Kalimantan, they have generated only 7,420MW and 1,819MG respectively. Compared to Java (smaller island seemingly :D), Java has almost 32MW electricity generated! A bit reminder, Sumatra and Kalimantan are where the main CBM resources located.
I am really hoping that my research will help the country to develop its CBM industry to improve the welfare of the society :).
Summary
- CBM potential resources in Indonesia is 453Tcf
- They are located in Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, and Sulawesi. The most CBM resources are in Sumatra and Kalimantan.
- Coal rank for CBM in Indonesia is a low rank and mostly subituminous (similar to Powder River Basin in the US) & bituminous.
- CBM is expected to fulfil the domestic needs, power and electricity.
Again, I hope you enjoy this blog and get something useful from it.
References
- Cbmasia.ca. (2016). CBM ASIA. [online] Available at: http://www.cbmasia.ca/CBM-In-Indonesia# [Accessed 12 Apr. 2016].
- Flores, R. (2004). Coalbed Methane in the Powder River Basin, Wyoming and Montana: An Assessment of the Tertiary-Upper Cretaceous Coalbed Methane Total Petroleum System. U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS–69–C. [online] Denver: U.S. Geological Survey, p.34. Available at: https://pubs.usgs.gov/dds/dds-069/dds-069-c/REPORTS/Chapter_2.pdf [Accessed 4 Nov. 2016].
- Harrington, J. (2016). CBM Indonesia – Dull Past, Bright Future. In: 2016 Technical Symposium. Jakarta: Indonesia Petroleum Association
- International Energy Agency (2014). Energy Supply Security. Indonesia. Paris: International Energy Agency, p.22.
- Mastalerz, M. (2014). Coal Bed Methane: Reserves, Production and Future Outlook. 2nd ed. London: Elsevier, pp.145-158.
- Stevens, S. and Hadiyanto (2004). Indonesia: Coalbed Methane Indicators and Basin Evaluation. In: SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers.
- Stevens, H., Scott, H., Sani, K. and Hardjosuwiryo, S. (2001). Indonesia’s 337 TCF CBM Resource a Low Cost Alternative to Gas, LNG. Oil and Gas Journal, (October 22).
- Tharakan, P. (2015). Summary of Indonesia’s Energy Sector Assessment. No. 09, December 2015. Manila: Asian Development Bank, p.14.
- Wkmigas.com. (2017). Working Area CBM | wk migas. [online] Available at: http://www.wkmigas.com/about-working-area/about-wk-cbm/ [Accessed 20 Mar. 2017].
- Wood Mackenzie (2015). Sumatra CBM. United Kingdom: Wood Mackenzie.


